Indian Cinema as Economic Catalyst
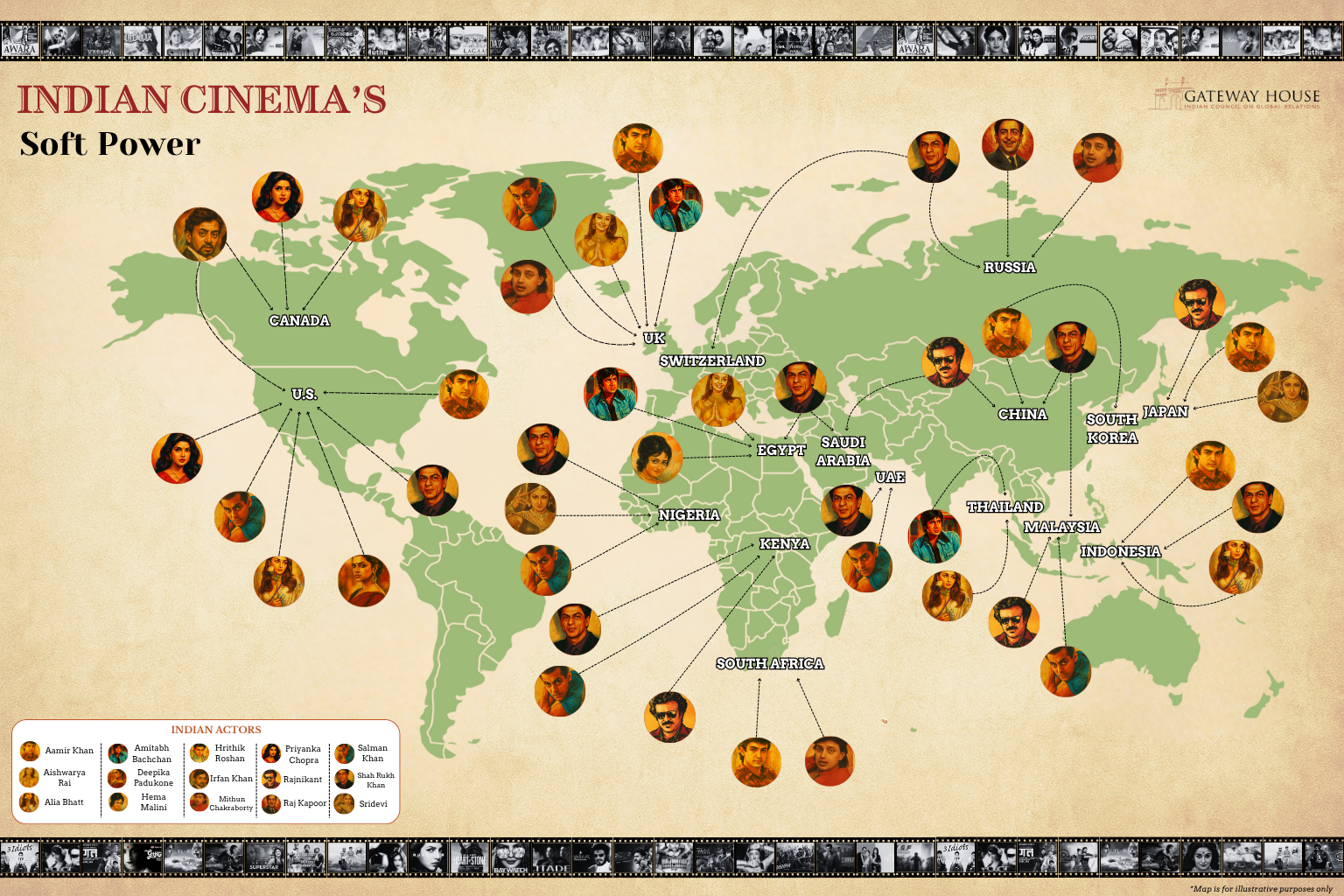
As India seeks leadership in a multipolar world, cultural credibility is as vital as economic clout. Cinema gives India an edge with vivid storytelling, music, and empowering narratives, fostering understanding in a polarised world. Its popularity correlates with trade, as seen in the U.S., Russia, and Middle East. The more popular the cinema, the bigger the boost to trade.




![EuropeProtests-01[85] copy](https://www.gatewayhouse.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/EuropeProtests-0185-copy.png)