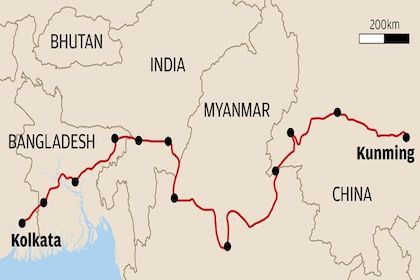
Physical connectivity in the Bay of Bengal
China is a clear winner in the physical connectivity stakes in the Bay of Bengal, and there's a reason a why: Its projects are connected to one another, from rail to road to port. While India also has some successful cross-border road and rail infrastructure projects, they are often an extension of an existing railway line or highway, not specific to the connectivity needs of the region. India can win by focussing instead on building infrastructure to maximise the vast maritime potential of the Bay of Bengal, especially the Andaman and Nicobar Islands that give India access to critical sea channels and trade routes.