Does the WTO have a future?
Don Stephenson, former Chief Trade Negotiator, India-Canada Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement, discusses how India and Canada can work together on effecting reform in the World Trade Organization
Don Stephenson, former Chief Trade Negotiator, India-Canada Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement, discusses how India and Canada can work together on effecting reform in the World Trade Organization
Rohinton Medhora, President, Centre for International Governance Innovation (CIGI), Waterloo, Canada, and co-host of the second edition of the India-Canada Track 1.5 Dialogue in Mumbai, spoke to Gateway House on how data management and governance around new technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence, are the issues of the future
 Courtesy: Flickr/MEA
Courtesy: Flickr/MEA
The India-Canada Track 1.5 Dialogue on Innovation, Growth and Prosperity, an initiative agreed upon in February 2018 by the two prime ministers, provides an opportunity for the bilateral relationship to grow through geopolitical convergence, greater economic collaboration and people-to-people interaction. A statement by External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar for the second edition of the Dialogue, held in Mumbai on 22 November 2019
 Courtesy: Flickr/MEA
Courtesy: Flickr/MEA
It’s time to start moving on matters in which Canada is a natural ally for India - trade liberalization, energy investments, intellectual property and the rules around e-commerce in particular and big data governance in general.
 Courtesy: MEA/Flickr
Courtesy: MEA/Flickr
The 2019 G20 Summit in Osaka on June 28-29, is the 14th meeting of the Group of 20 leaders. The G20 is the world’s most influential economic multilateral forum. It is the agenda-setting forum that develops and guides rules of global economic governance. Under the Japanese Presidency, this summit will be the first to discuss and establish the rules for the worldwide governance of data, including current hot-button issues like data localisation and data sovereignty. India has both a preparatory and a contributory role to play in the G20 this year. For in 2022, it will be the President of the G20. India must identify its agenda early on; its a weighty responsibility but also an opportunity to set the global economic agenda.
 Courtesy: Gateway House & CIGI
Courtesy: Gateway House & CIGI
The virtual computer world holds tremendous potential for harm infliction, and cybercrime is a growing concern for India and Canada. Both countries have cracked down on digital black markets, where transactions for contraband and illegal services take place, but such cooperation can be further deepened through advanced use of technology and informal collaboration, for example, thereby also contributing to international security at the multilateral level
 Courtesy: Wikimedia Commons
Courtesy: Wikimedia Commons
The United States, Europe and the Asia Pacific today form Canada’s tripartite foreign policy priorities. The ASEAN is its sixth largest partner, which was not so 20 years ago, but economic engagement with India – still small, compared to China and Japan – has scope to grow
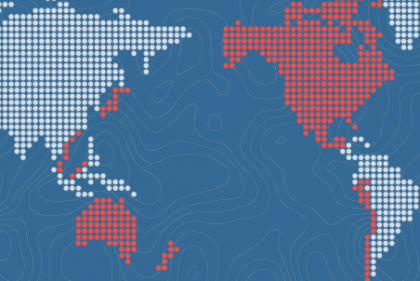 Courtesy: ustr.gov
Courtesy: ustr.gov
The Trans-Pacific Partnership has dropped strong Intellectual Property Rights regulations on India’s doorstep. The implications of these regulations could affect India’s own policies, as well as her global aspirations towards the potential Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership.
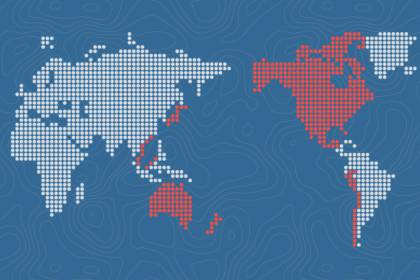 Courtesy: ustr.gov
Courtesy: ustr.gov
The U.S.-driven Trans Pacific Partnership agreement between 12 countries, which is aiming to become the new standard of world trade, impacts domestic systems globally. For India, it will skew investment and intellectual property rights, and especially the debate over the Investor State Dispute System which allows companies to challenge sovereign rights and public policy.
 Courtesy: Wikipedia
Courtesy: Wikipedia
Although it is too soon to comprehensively analyse the Trans-Pacific Partnership agreement of October 5, it is worth assessing what is known. Here are the facts, the controversies, the assessments, and the implications for countries that are not part of the agreement, especially India.