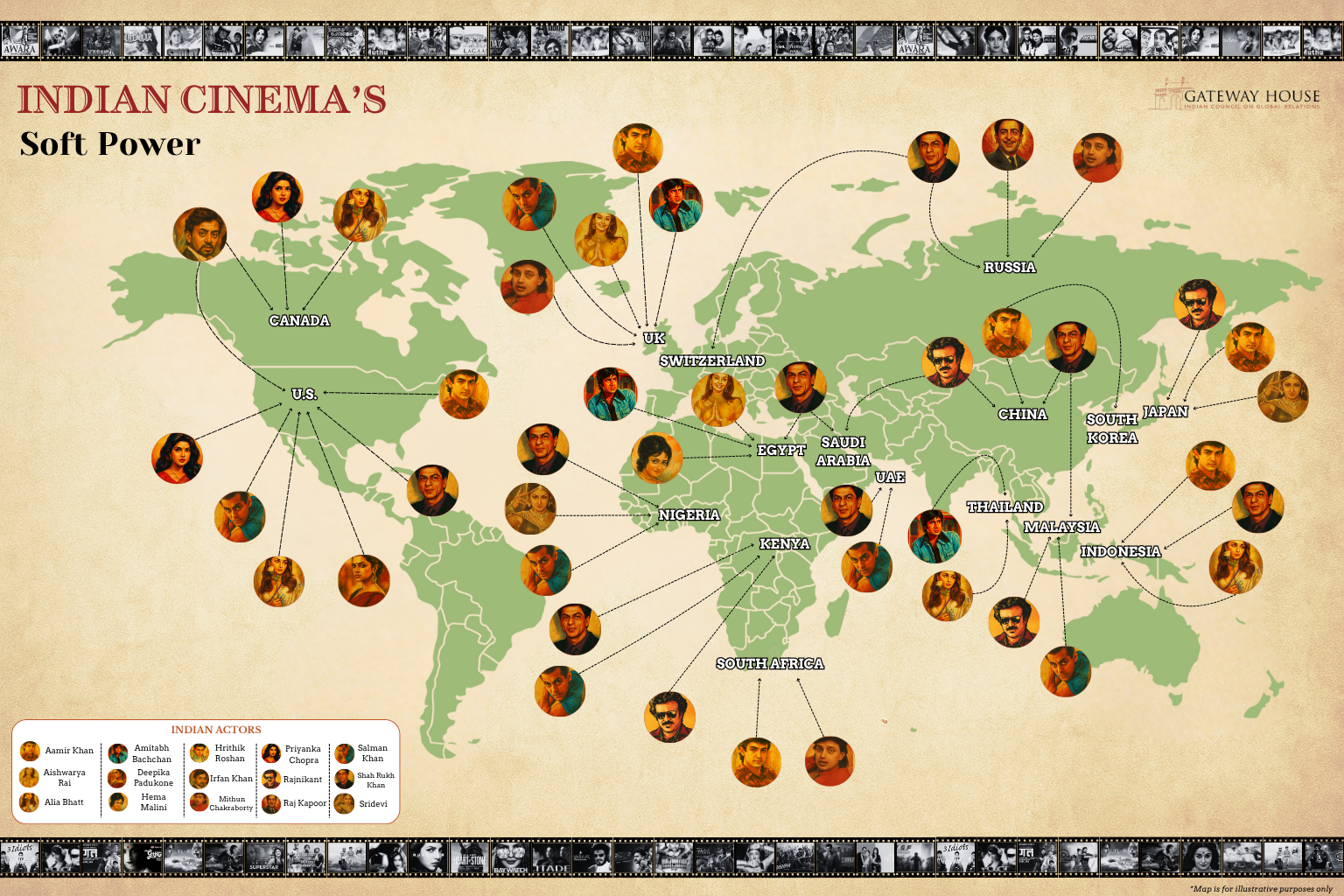
Unseen opportunities in UK-India trade
UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer is in India Oct 8-9, to discuss geopolitics with his Indian counterpart and also to boost bilateral trade. The UK-India Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) signed in July 2025 marks a milestone in the relationship. The deal, however, omits reference to the creative industries which contribute significantly to UK GDP and play a vital role in the UK-India corridor.