1. Introduction
Schneider Electric is a French company that provides energy, automation, and digital solutions for efficiency and sustainability. By combining energy technologies, real-time automation software and related services, Schneider Electric provides solutions for digital infrastructure requirements across industries, data centres, as well as private residences, buildings, etc.
As a leading manufacturer of critical components, hardware systems and software used in a range of industrial automation and control applications, Schneider Electric is in a unique position to accelerate Industry 4.0 adoption, by building a manufacturing factory infrastructure that is ready for automation and data generation. The types of products offered are covered in Table 1.
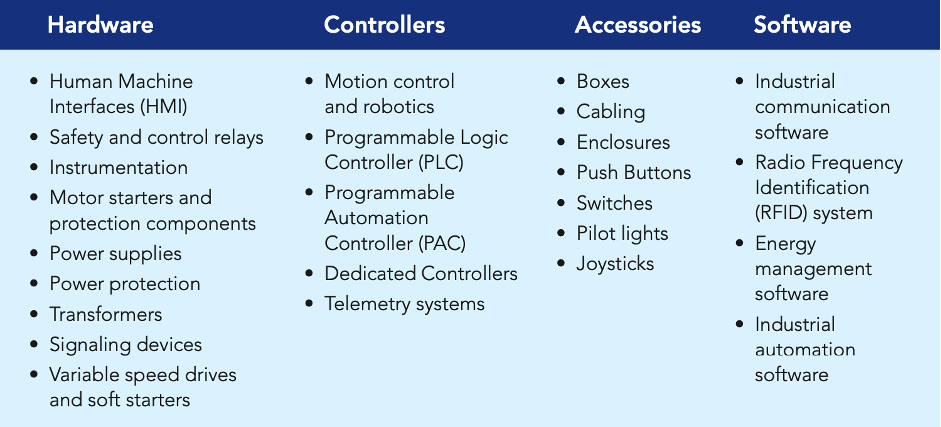
The wide range of the company’s products solutions and services, also give it an unparallel domain expertise. This has allowed Schneider Electric to develop an end-to-end, patented, digital architecture platform called EcoStruxureTM that delivers IoT-enabled solutions to various industries. The platform has been deployed at more than 4.8 lakh sites, globally.
Schneider Electric’s solutions are applicable not just on the factory floor but also for a series of nodes within the digital value chain. As a result, the company has jumped to 4 on the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 for the year 2020, from 11 in 2019. Equipped with the EcoStruxureTM platform, between 2017 and 2019 Schneider Electric launched 17 smart factories around the globe including three facilities in India, at Hyderabad, Bengaluru and Mumbai.
In India, Schneider Electric has a total of eight manufacturing plants. Of these, the switchgear manufacturing plant in Hyderabad, commissioned in 2006, has become the first Indian facility to join the smart factory network in Feb 2019. This was followed by the Bengaluru facility in Nov 2019.
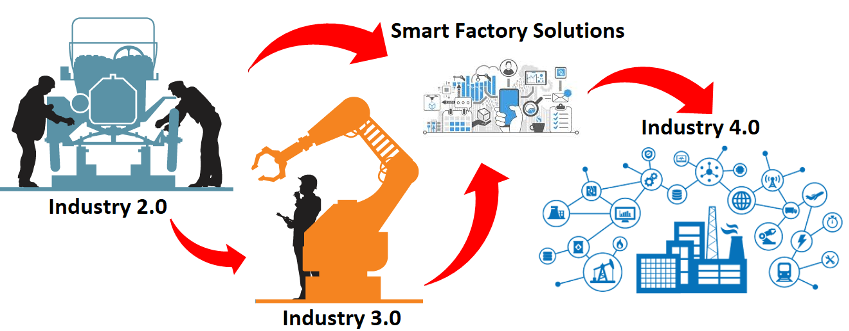
2. Smart Factory Solutions Enable Industry 4.0
Industry 3.0 saw the rapid deployment of automation within manufacturing lines using PLCs, PACs, SCADA and sensorisation of process lines. Industry 4.0 relies heavily on data analytics to develop Business Intelligence (BI). Smart Factory solutions such as EcoStruxureTM, not only help to bring Industry 3.0 compliant facilities to Industry 4.0 readiness, but can also assist older facilities with low automation and data generation capabilities, to leapfrog to Industry 4.0 readiness, albeit with greater investment in digital and Information and Communications Technology (ICT) infrastructure, upgrade.
Source: Tata Steel
Data generated across various nodes in the value chain in a manufacturing factory, need to be connected over a platform to enable centralised data analytics. The EcoStruxureTM platform with its open architecture permits integration of IoT solutions even with legacy components, and connects plant assets on the shop floor, to the enterprise and supply chains. The open architecture capabilities of the EcoStruxureTM platform substantially reduce the cost of digital transformation.
3. Transformation Philosophy
Eat your own food: Schneider Electric is the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) of critical automation and IIoT hardware components. This unique knowledge and expertise allow the group in a position to follow an ‘Eat your own Food’ philosophy for designing and developing digital smart factory solutions in-house. These solutions build on hardware and software originating from a single source brings in high degree of reliability in performance and post-sale service.
Pankaj Goyal, Vice President, EcoStruxureTM and Digital, Schneider Electric, India, states that a multipronged strategy is essential for accelerating Industry 4.0 product development. At Schneider Electric, this strategy is primarily driven through acquisitions, outsourcing to start-ups and utilising commercially available technology.
In Sep 2017, Schneider Electric reverse acquired U.K. based Aveva, an engineering software developer, and merged its software division with Aveva. This merger has been a primary contributor towards product development.
4. Methodology
A smart factory is essentially a facility that is capable of generating data in every process of the value chain. The capability of a factory to generate data is directly proportional to its depth and spread of automation and sensorisation. A Smart Factory platform and architecture such as EcoStruxureTM can aid manufacturing units to progress on the path of automation, sensorisation and provide connectivity for enterprise-wide operations.
- EcoStruxureTM: The EcoStruxureTM architecture and platform provides IoT enabled solutions for various verticals, which are referred to as Lean Digitisation Systems (LDS). These include:
- EcoStruxureTM Building:This is used for facility management, and improves the engineering efficiency of the building, ensuring productivity, safety and comfort for occupants.
- EcoStruxureTM Grid: This is used for seamless connectivity between local power production and integration at the grid edge, thereby bridging demand and supply. This LDS aids in increasing the power grid’s efficiency.
- EcoStruxureTM Power: This digitises and simplifies medium and low-voltage electrical distribution systems. It provides actionable data that help in decision making that can protect people, safeguard assets, maximize operational efficiency and enhance business continuity.
- EcoStruxureTM Plant & Machine: This is most suited for digital manufacturing. It provides digital transformation solutions for various processes in the manufacturing value chain and connects them across the company.
- EcoStruxureTM IT: This caters to the data center’s physical infrastructure and provides extendibility to future demand driven by IoT, growth in the cloud, and edge computing technologies without compromising operational efficiency.
- Architecture: The architecture of a manufacturing line needs to monitor Man, Material, Machine and Process. This can be achieved by applying a range of EcoStruxureTM LDS at level zero, that bring in connectivity between shop floor assets and beyond. At Schneider Electric, Hyderabad, the Layer 1 and Layer 2 components are a mix of proprietary and commercially available solutions and products. A basic architecture structure is shown in figure 2.

Source: Schneider Electric, India
5. Success Stories
Of the 17 Schneider Electric smart factories equipped with EcoStruxureTM, two facilities – one each in France and Indonesia have been able to scale-up to an Industry 4.0, World Economic Forum (WEF) recognised Global Lighthouse Network.
Some of the major benefits accrued at Schneider Electric ‘smart factories’ are outlined in Table 2.

Source: Schneider Electric
EcoStruxureTM can be leveraged for the following benefits within an enterprise:
- Agile management and improved process visibility
- Life cycle and maintenance management
- Man-machine-process integration
- Facilitating preventive, predictive and prescriptive maintenance
- Empowering operators
- Improving reliability
- Traceability of product
- Supplier-manufacturer-customer connection
- Bringing standardisation across manufacturing facilities
- De-skilling the process to make it error proof
6. Key Findings
MNC Centric
- Adoption of EcoStruxureTM LDS has helped three of the 17 Schneider Electric smart factories scale-up to Industry 4.0, WEF recognised, global lighthouse networks within the span of two years. The EcoStruxureTM platform’s open architecture offers plug-and-play solutions across a range of verticals, thereby reducing the time and cost of transformation.
- Adoption of digital solutions will result in increased productivity and savings. These savings can then spur capital expenditure within the enterprise for creating productivity linked infrastructure and aid job creation.
MSME Centric
Schneider Electric’s views on adoption of Industry 4.0 solutions by MSMEs are:
- MSMEs in the value chains of Schneider Electric have shown a keen interest in absorbing digital solutions to bring about enhanced connectivity with the parent enterprise.
- The MSME sector in India is an untapped market for EcoStruxureTM products. Lack of awareness and limited capital availability, are challenges that hinder growth of Industry 4.0 solutions within MSMEs.
- Micro and to some extent small-scale industries, must focus on adopting commercially available solutions targeted at external nodes within the value chain.
Commander Amrut Godbole is Fellow, Indian Navy Studies Programme at Gateway House.
Manjeet Kripalani is Executive Director and co-founder at Gateway House.
Sagnik Chakraborty is Former Researcher, Cybersecurity Studies Programme at Gateway House.
This study was conducted by Gateway House, in partnership with India EXIM Bank. Read the full study here.
For interview requests with the authors, or for permission to republish, please contact outreach@gatewayhouse.in.
Disclaimer: The contents of the paper are personal views of the author and do not reflect the official position of the Indian Navy or Government of India.
© Copyright 2021 Gateway House: Indian Council on Global Relations. All rights reserved. Any unauthorized copying or reproduction is strictly prohibited.


