Prime Minister Narendra Modi has capped off 2015–a very busy year–with an ultimately diplomatic coup–an unscheduled stopover in Pakistan.
2015 was the year when India’s foreign policy began to consolidate, a year during which the “Modi doctrine” was put into action. It’s a doctrine that raises the country’s global profile in terms of its strategic economic and security requirements, and positions India as the big player in South Asia.
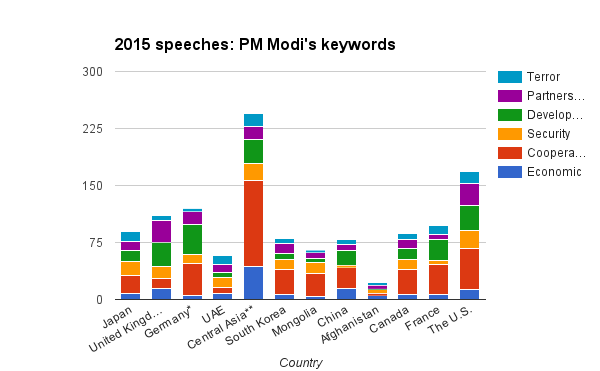
It was a very busy year. Prime Minister Narendra Modi clocked an estimated 1,40,000 kilometres to become India’s—maybe the world’s—platinum premier frequent flier. Gateway House analysed the speeches made by Modi during these visits abroad in 2015. We picked his most often-used terms to conclude that India’s foreign policy is all about forging new and improved global political and economic partnerships.
The prime minister began the year with a visit to Seychelles, Mauritius, and Sri Lanka. There, he focused on the economy, terrorism, and security. These themes continued into his visits to France, Germany, Canada, China, the U.S, and other counties, as outlined below:
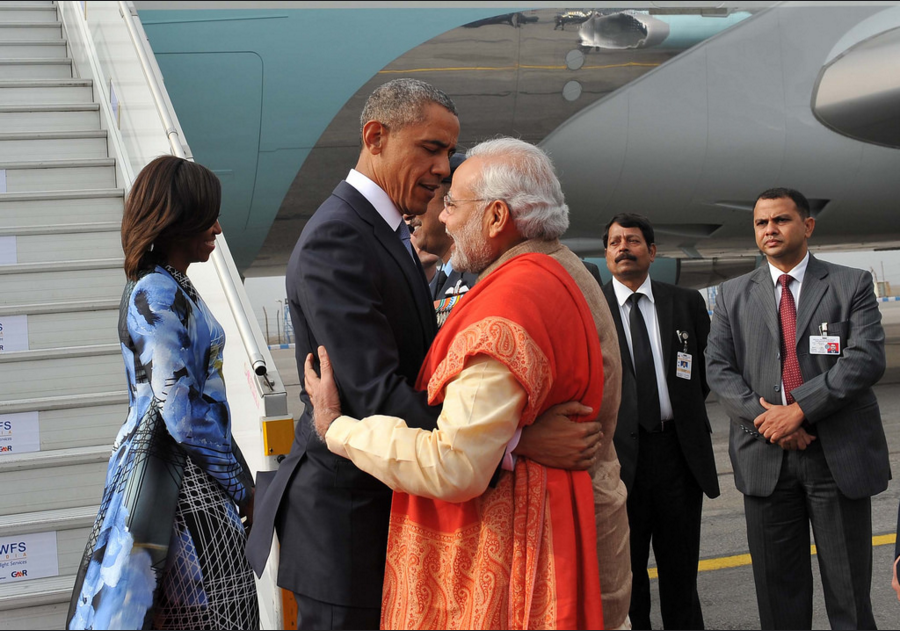
U.S.
The year began with President Barack Obama as chief guest—at Modi’s invitation—at the Republic Day parade in New Delhi on 26 January. The economic dimension of the bilateral relationship was a constant, and that was the focus even when Modi visited the U.S. in September. The two leaders revived a relationship that had fallen into disrepair, and which is now humming along with a vibrant partnership spanning military and economic ties. But the usual top three disagreements remain – IPR/pharmaceuticals, H1-B visas/IT professionals, and terrorism/Pakistan.
Through the year-long bilateral conversations, key words like ‘cooperation’, ‘development’, and ‘partnership’ ruled the charts with 54, 33, and 28 mentions respectively, in his speeches and joint statements. ‘Strategic’ appeared 15 times in three joint statements issued in January 2015. ‘Terror’ and the attendant platitudes, too, had a significant resonance, with 16 references in Modi’s speeches and the joint statements between India and the U.S.

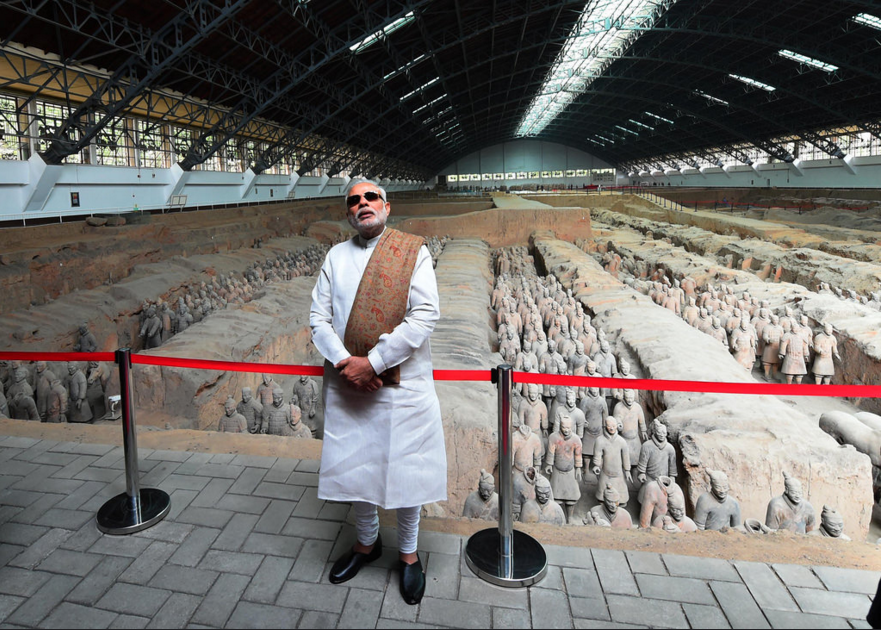
China
In May, Modi reciprocated President Xi Jinping’s 2014 visit to India by heading to Beijing. A photograph of Modi wearing sunglasses in the museum of terracotta soldiers elicited an avalanche of tweets back at home.
The two countries issued two joint statements, including one on climate change. The theme of Modi’s vocalisations remained the economic aspects of the bilateral relationship. ‘Cooperation’, ‘development’, and ‘economic’ topped the list of words used in his speeches, with 29, 20 and 14 appearances, respectively. ‘Strategic’ was uttered five times, and ‘security’ came last with only three mentions in speeches as well as the joint statement.

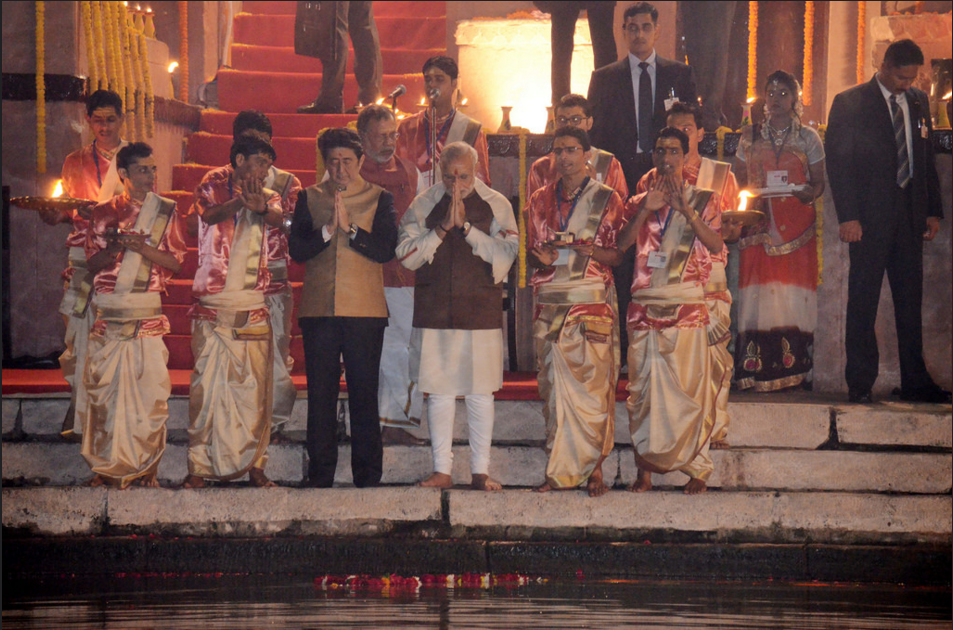
Japan
In contrast was Modi’s public display of affection for Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, who was in India recently—a close second to Modi’s friendship with Obama. The son et lumiere at Varanasi apart, Abe and Modi had a serious agenda: investments and the security of the South China Sea. Japan joined India for the first time in the annual Malabar exercise with the U.S. The trio sent a clear message to China that its shenanigans in the eastern waters—which India once also significantly called the West Philippines Sea—won’t be tolerated.
In the joint statement issued on 12 December 2015, ‘security’ was mentioned 18 times, followed by nine iterations of ‘economy’/’economic’. ‘Strategic’ too was there nine times in the two joint statements issued by the two leaders. There were 24 references to ‘cooperation’, followed by ‘development’ and ‘investment’ at 14 times each.

Germany
The themes of investment and technology also featured during Modi’s visit to Germany, where he dramatically launched the Make In India campaign at the Hannover Messe in June, with German chancellor Angela Merkel in attendance. It was a hotbed of activity, with car-maker Volkswagen showcasing its Vento model, now being exported to global markets from India. Merkel reciprocated by a visit to India in the first week of October for the third India-Germany inter-governmental consultations.
The word ‘partnership’ was mentioned 12 times in the joint statement and ‘economy’ got six mentions. But the winners were ‘cooperation’ with 31 references, and ‘development’ at 29, followed by ‘security’ and ‘investment’ at 10 and 8, respectively.
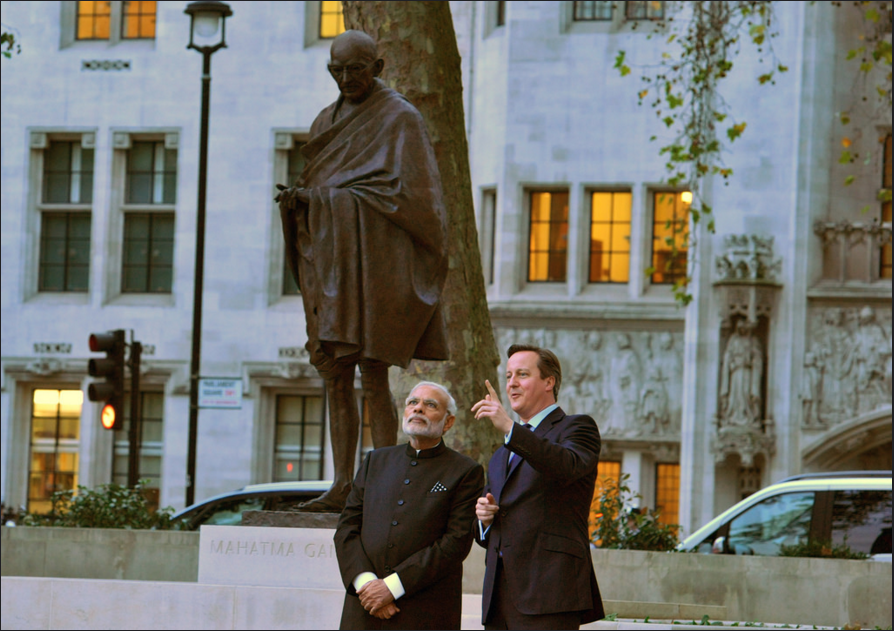
UK
In 2015, the colonial equation was reversed: Modi made history as the first Indian prime minister to address the British parliament—a sweet moment for an India once ruled by the UK. It is all the more so because the Tata group is now the largest private sector employer in the UK. Modi lunched with the British monarch and unveiled a statue of Mahatma Gandhi, whose satyagragha decades ago drove the same colonisers out of India. Modi followed it up with his usual rock concert-like public address to some 60,000 British Indians at Wembley stadium.
The trip elicited six joint statements—the most this year from a single state visit—including one on energy and climate change, and another on defence and the international security partnership. As expected ‘investment’, ‘economic’, ‘growth’, and ‘development’ were repeated 19, 15, 13, and 31 times, respectively. ‘Partnership’, ‘security’, and ‘cooperation’ showed up 29, 16, and 13 times each.

South Asia
Modi’s most critical diplomacy overtures were with South Asian countries. After the launch of the SAARC (minus Pakistan) road connectivity agreement in Nepal in 2014, and a strong helping hand through the calamitous earthquake in that country in April this year, the Nepal-India bilateral took a dive after Nepal’s new Constitution was introduced.
To the east, Modi kept a long-standing promise to Indians stranded in Bangladesh’s enclaves by signing the Land Boundary Agreement. His June visit to Dhaka was replete with terms like ‘economy’, ‘cooperation’, and ‘investment’. It was a show of support to Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina, who is valiantly battling extremism.
Sri Lankan President Maithripala Sirisena’s chose India as his first stop after his electoral victory. Immediately after his February visit, Modi called on Sirisena in Colombo in March. Modi stressed on the ocean economy, tourism, and a shared commitment to stronger economic cooperation. Apart from a $318 million line of credit to enhance Sri Lanka’s railway network, he emphasised ‘peace’ in Sri Lanka (five times) and focused on the ‘economy’/’economic’, which featured four times in his speech. ‘Cooperation’ appeared four times too, and ‘development’ twice.
In 2016, Modi will visit Pakistan, and the groundwork has started with the resumption of bilateral talks. His envoy, Minister of External Affairs Sushma Swaraj, met her counterpart in Islamabad, and Modi’s confidant and National Security Adviser Ajit Doval met his counterpart in Bangkok.
At the tail end of 2015
As the year draws to a close, Modi made an unscheduled stopover to Pakistan sending the media and analysts in an overdrive. The contours of the hour-long meeting at Pakistan Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif’s residence aren’t known. Off the planned foreign trips, Modi visited old friend Russia, during which the friendship was reiterated. His discussions with President Vladimir Putin also focussed on defence ties, the ISIS threat, and the Syrian crisis. Expectedly, ‘security’, ‘cooperation’, and ‘economy’ were the key words in the joint statements.
On Christmas day, Modi will leave Moscow via Kabul, where he will inaugurate Afghanistan’s India-built Parliament building.
That makes it 26 countries visited in one year—and qualifies Modi to the title of the ‘most-travelled head of state in the world’. Others follow, some quite far behind: Japan’s Prime Minister Shinzo Abe with 23 foreign trips; Chinese president Xi Jinping with 14 overseas trips; and U.S. President Barack Obama with just 11 foreign visits.
India has historically punched below its weight in the global arena, and Modi’s travels indicate that he intends to change this equation. India’s economic and demographic weight is now being used in its favour in major global forums like the G20, COP21, ASEAN, and on international security issues.
The Indian economy is now the fastest-growing of the major economies, and this advantage was reflected in Modi’s speeches during his two dozen international visits. The keywords of these—as listed here—speak of a consolidating strategy.
Shubhashish is Website and Content Editor at Gateway House.
This article was exclusively written for Gateway House: Indian Council on Global Relations. You can read more exclusive content here.
For interview requests with the author, or for permission to republish, please contact outreach@gatewayhouse.in.
© Copyright 2015 Gateway House: Indian Council on Global Relations. All rights reserved. Any unauthorized copying or reproduction is strictly prohibited


